Bond yields and prices are important concepts for investors to understand when evaluating the potential returns of different bond investments. In this article, we’ll explain how to calculate and compare bond yields and prices and how they are related to one another.
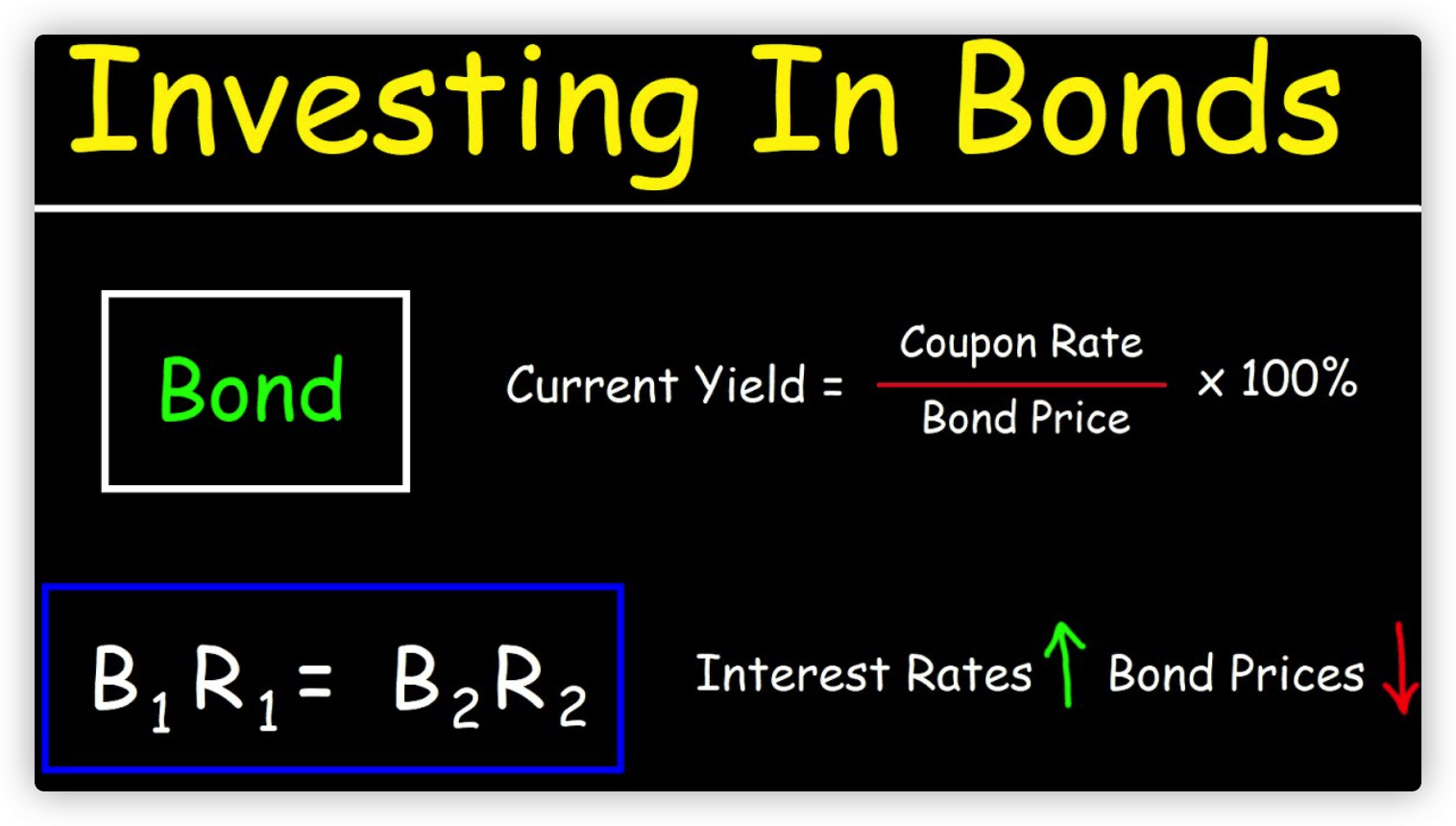
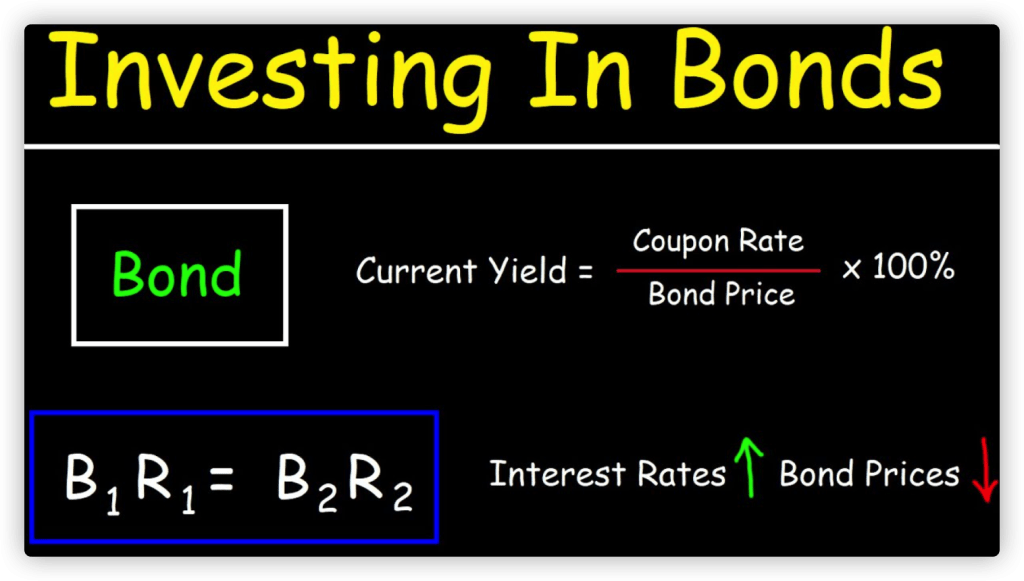
Bond yield is a measure of the return on a bond investment, expressed as a percentage of the bond’s price. It represents the annual interest payment on the bond divided by the bond’s price. For example, if a bond has a yield of 3% and a price of $100, it would pay an annual interest payment of $3.
Bond prices and yields have an inverse relationship, meaning that when bond prices rise, yields fall, and when bond prices fall, yields rise. This is because bond yields are calculated as a percentage of the bond’s price, so when the price goes up, the yield goes down, and vice versa.
To calculate the yield on a bond, you can use the following formula:
Yield = Annual interest payment / Bond price
For example, if a bond has a price of $100 and an annual interest payment of $5, its yield would be 5% ($5 / $100 = 0.05).
To compare the yields of different bonds, you can use the yield to maturity (YTM) calculation, which takes into account the bond’s current price, interest payments, and maturity date. The YTM is the total return an investor can expect to receive if they hold the bond until it matures.
To calculate the YTM of a bond, you can use a bond yield calculator or use the following formula:
YTM = [C + (F – P) / N] / [(F + P) / 2]
Where:
C = annual interest payment
F = face value
In conclusion, bond yields and prices are important concepts for investors to understand when evaluating the potential returns of different bond investments. Bond yields are calculated as a percentage of the bond’s price and represent the annual interest payment on the bond. Bond prices and yields have an inverse relationship, meaning that when bond prices rise, yields fall, and when bond prices fall, yields rise. To compare the yields of different bonds, investors can use the yield to maturity (YTM) calculation, which takes into account the bond’s current price, interest payments, and maturity date. It’s important for investors to carefully consider the risks and rewards of different bond investments and to choose investments that align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.